The Cupid Peptide Company
EXPERTS IN CELL PENETRATING PEPTIDE
CUSTOM DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE
MDM2
Mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase, and considered a hub cancer protein due to its capacity to interact with a large number of different partners of which p53 is most well described. These protein interactions are central in modulating the growth and malignancy of cancers. The MDM2-p53 interaction is very complex involving multiple levels of regulation by numerous cellular proteins and epigenetic mechanisms. It is hoped that understanding the pathway regulating the MDM2-p53 axis may enable it to be exploited for anticancer therapy (1-4).
Reviews
1) MDM2's social network. Fåhraeus R, Olivares-Illana V. Oncogene. 2013 Oct 7. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.410
2) MDM2, MDMX and p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Wade M, Li YC, Wahl GM. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Feb;13(2):83-96. doi: 10.1038/nrc3430. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Review.
3) The Interaction Between FAK, MYCN, p53 and Mdm2 in Neuroblastoma. Waters AM, Beierle EA. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Sep 10.
4) The MDM2-p53 pathway revisited. Nag S, Qin J, Srivenugopal KS, Wang M, Zhang R. J Biomed Res. 2013 Jul;27(4):254-71. doi: 10.7555/JBR.27.20130030
MDM2 interactions
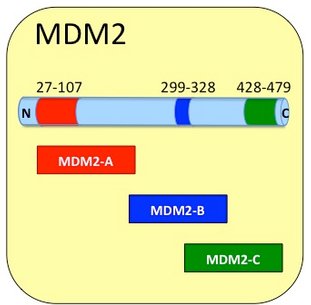
Wikipedia lists over 30 proteins that MDM2 is thought to interact with (1). Of these the most studied is the Mdm2 - p53 interaction between the N-terminal region of MDM2 binding to the N-terminal transactivation domain of p53 (2,3). This interaction causes p53 repression which is of major interest to Cancer therapy. This region is contained in Product: Cupid-MDM2-A.
At the C-Terminal of MDM2 there is a RING domain. This region has been shown to have several functions. It is associated with an intrinsic E3 ligase activity and acts as an oligomerization domain, binding MDM2 with either another MDM2 molecule or with a similar region in the MDMX protein (4,5). This region is known to bind potential ubiquitinoylation substrates such as the RASSF1A protein (6).This region is contained in Product: Cupid-MDM2-C.
The Central part of the molecule features a Ran Binding-Protein Motif but is more enigmatic in its associations. It has been suggested to contain a second binding site for p53, is known to interact with several proteins, including p300, YY-1, ARF, ribosomal protein L11, PA28, nbs1 and KAP1 and the acidic region it contains (aa 254–264) is necessary and sufficient for Rb binding and subsequent degradation (7-11). This region is contained in Product: Cupid-MDM2-B.
Cupid Cargo MDM2-A
LVRPKPLLLKSVGAQKDTYTMKEVLFYLGQYIMTKRLYDEKQQHIVYCSNDDLLGDLSGVPSFSVKEHRKIYTMIYRNL
Amino acids 27 to 107 (81 amino acids)
SWIB Motif, SWIB / MDM2 domain (P53 binding)
Cupid Cargo MDM2-B
LADYWKCTSCNEMNPPLPSHCNRCWALREN
Amino acids 299 to 328 (30 amino acids)
zfRAN Binding Protein motif, Zn-finger in Ran binding protein
Cupid Cargo MDM2-C
SSLPNAIEPCVICQGRPKNGCIVGHKTGHLMACFTCAKKLKKRNKPCPVCR
Amino acids 428 to 479 (52 amino acids)
zfC3HC4 Motif, Zinc finger, C3HC4 type (RING finger)
References
(1) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mdm2
(2) p53: an overview of over two decades of study. Cheah PL, Looi LM. Malays J Pathol. 2001 Jun;23(1):9-16. Review.
(3) Targeting the MDM2-p53 interaction for cancer therapy. Shangary S, Wang S. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Sep 1;14(17):5318-24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5136. Review.
(4) MdmX is a RING finger ubiquitin ligase capable of synergistically enhancing Mdm2 ubiquitination. Badciong JC, Haas AL. J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 20;277(51):49668-75. Epub 2002 Oct 21.
(5) Structure of the MDM2/MDMX RING domain heterodimer reveals dimerization is required for their ubiquitylation in trans. Linke K, Mace PD, Smith CA, Vaux DL, Silke J, Day CL. Cell Death Differ. 2008 May;15(5):841-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402309. Epub 2008 Jan 25
(6) The tumour suppressor RASSF1A promotes MDM2 self-ubiquitination by disrupting the MDM2-DAXX-HAUSP complex. Song MS, Song SJ, Kim SY, Oh HJ, Lim DS. EMBO J. 2008 Jul 9;27(13):1863-74. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.115. Epub 2008 Jun 19.
7) Multiple interacting domains contribute to p14ARF mediated inhibition of MDM2. Clark PA, Llanos S, Peters G. Oncogene. 2002 Jul 4;21(29):4498-507.
8) Retinoblastoma protein modulates gankyrin-MDM2 in regulation of p53 stability and chemosensitivity in cancer cells. Qiu W, Wu J, Walsh EM, Zhang Y, Chen CY, Fujita J, Xiao ZX. Oncogene. 2008 Jul 3;27(29):4034-43. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.43. Epub 2008 Mar 10.
(9) Proteasome activator PA28 gamma regulates p53 by enhancing its MDM2-mediated degradation. Zhang Z, Zhang R. EMBO J. 2008 Mar 19;27(6):852-64. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.25. Epub 2008 Feb 28.
(10) Mdm2 promotes genetic instability and transformation independent of p53. Bouska A, Lushnikova T, Plaza S, Eischen CM. Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Aug;28(15):4862-74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01584-07.
(11) p300/MDM2 complexes participate in MDM2-mediated p53 degradation.Grossman SR, Perez M, Kung AL, Joseph M, Mansur C, Xiao ZX, Kumar S, Howley PM, Livingston DM. Mol Cell. 1998 Oct;2(4):405-15.