The Cupid Peptide Company
EXPERTS IN CELL PENETRATING PEPTIDE
CUSTOM DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE
Reviews
(1) "IKK-gamma is an essential regulatory subunit of the IkappaB kinase complex". Rothwarf DM, Zandi E, Natoli G, Karin M (1998). Nature 395 (6699): 297–300. doi:10.1038/26261. PMID 9751060.
(2) Complementation cloning of NEMO, a component of the IkappaB kinase complex essential for NF-kappaB activation. Yamaoka S, Courtois G, Bessia C, Whiteside ST, Weil R, Agou F, Kirk HE, Kay RJ, Israël A. Cell. 1998 Jun 26;93(7):1231-40. PMID: 9657155 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Free Article
(3) The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. Hinz M, Scheidereit C. EMBO Rep. 2014 Jan;15(1):46-61. doi: 10.1002/embr.201337983. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Review. PMID: 24375677 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
(4) Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Napetschnig J, Wu H. Annu Rev Biophys. 2013;42:443-68. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130338. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Review. PMID: 23495970 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Free PMC Article
(5) Ubiquitination in signaling to and activation of IKK. Chen ZJ. Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):95-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01108.x. Review. PMID: 22435549 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Free PMC Article
(6) The zinc finger domain of IKKγ (NEMO) protein in health and disease. Shifera AS. J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Oct;14(10):2404-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01054.x. Review. PMID: 20345847 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
Nemo interactions
The essential function of NEMO is thought to act as a polyubiquitin binding factor which recruits the IKK complex to polyubiquitin scaffolds that have formed following receptor-initiated signaling. Wikipedia lists a dozen proteins that bind to Nemo (1)
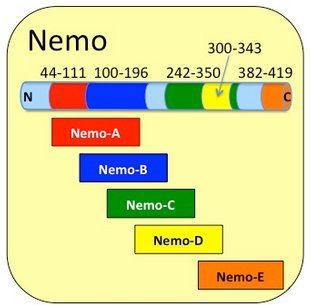
The amino-terminal α-helical region is followed by a coiled-coil domain (CC1) from residues 44-196 that functions as the interaction interface with IKKα and IKKβ (the canonical IKKs) as well as TRAF proteins (TNF receptor associated factor) and as a dimerization region for Nemo itself (2, 3). The region is attached to two products: Cupid-Nemo-A (residues 44-111) and Cupid-Nemo-B (residues 100-196)
After this region is a stretch of residues (200-250) reported to interact with TANK protein (TRAF family member-associated NF-kappa-B activator) (3)
The central region contains another coiled-coil region (CC2) from residues 249-278 and a Leucine zipper (LZ) domain from residues 312-339. Together this region forms the ubiquitin-binding domain, UBAN (ubiquitin-binding in ABIN and NEMO, also AHD2, ABIN homology domain 2).
The region is represented in two products: Cupid-Nemo-C (residues 242-350) which contains Cupid-Nemo-D (residues 300-343)
At the extreme carboxyl terminus, there is a zinc-finger (ZNF) region that is very likely involved in mediating interactions with ubiquitinated proteins (4). It may be involved in interactions with substrates such IκBα (Inhibitor of κBα ) which are thought to mask the nuclear localization signals (NLS) of NF-κB proteins. The C-terminal part of NEMO is also involved in the oligomerisation of the protein.
The region is represented in the product Cup-Nemo-E (residues 382-419)
Using human protein microarrays, 112 NEMO binding proteins have been identified, including a large number of signaling kinases and proteins related to development and the cell cycle and cell resistance to apoptosis (5-8).
Finally, approaches using cell-permeable peptides have been used to successfully probe Nemo interactions in vivo (9)
Cupid NEMO Cargoes
Human NF-kappa-B essential modulator isoform a (NEMO)
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001093327.1
419 amino acids
Cupid Cargo NEMO A
EQGAPETLQRCLEENQELRDITQSNQILRERCEELLHFQASQREEKEFLMCKFQEARKLVERLGLEK
Amino Acids 44 to 111 (68 amino acids)
Dimerization Domain
Cupid Cargo NEMO B
ARKLVERLGLEKLDLKRQKEQALREVEHLKRCQQQMAEDKASVKAQVTSLLGELQESQSRLEAATKECQALEGRARAASEQARQLESEREALQQQHS
Amino Acids 100 to 196 (97 amino acids)
First Coil-Coil Domain
Cupid Cargo NEMO C
DNHIKSSVVGSERKRGMQLEDLKQQAEEALVAKQEVIDLKEEAEQHKIVMETVPVLKAQADIYKADFQAERQAREKLAEKKLLQEQLEQLQREYSKLKSCQES
Amino Acids 242 to 350 (109 amino acids)
Ubiquitin Binding Site
Nemo
NEMO, the NF-kB essential modulator (IKKγ), is a global transcriptional regulator found in most animal cells.
Nemo was originally described as being required for activation of the Nuclear Factor k-light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF- kB) pathway in response to a wide variety of stimuli, including cytokines such as TNFalpha, pathogens, free radicals, hypoxia, UV irradiation and other such stresses (1, 2). The genes activated by the NF-kB pathway are involved in inflammation, immunity, cell survival, and cross-talk between pathways and non-canononical events of the pathway impact disease states like cancer and diabetes (3).
A key step in the NF-kB signaling pathway is the regulation of the interaction between NF-kB and the inhibitory IkB family of proteins, by the IkB kinase (IKK) complex.
The IKK complex is a large assembly of proteins (700–900-kDa molecular mass) consisting of a homo- or hetero-tetramer of two types of catalytic subunits, IKKα and IKKβ, which are associated with two molecules of NEMO (IKKγ).
The IKK phosphorylates the inhibitory IkB subunit of the NF-kB·IkB complex in the cytoplasm. This phosphorylation marks IkB for degradation by the proteasome and releases NF-kB from the inhibitory complex. The freed NF-kB proteins are then transported into the nucleus where they bind to their target sequences and activate gene transcription (4-6).
Cupid Cargo NEMO D
VLKAQADIYKADFQAERQAREKLAEKKELLQEQLEQLQREYSKL
Amino Acids 300 to 343 (44 amino acids)
Leucine Zipper domain
Cupid Cargo NEMO E
PSQRRSPPEEPPDFCCPKCQYQAPDMDLQIHVMECIE
Amino Acids 382 to 419 (38 amino acids)
Zinc Finger domain
References
(1) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IKBKG
(2) "Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain". Deng, L; Wang C; Spencer E; Yang L; Braun A; You J; Slaughter C; Pickart C; Chen Z J (October 2000). Cell (UNITED STATES) 103 (2): 351–61. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00126-4. PMID 11057907.
(3) "Association of the adaptor TANK with the I kappa B kinase (IKK) regulator NEMO connects IKK complexes with IKK epsilon and TBK1 kinases". Chariot, Alain; Leonardi Antonio; Muller Jurgen; Bonif Marianne; Brown Keith; Siebenlist Ulrich (October 2002). J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (40): 37029–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205069200. PMID 12133833.
(4) "Mutations in the zinc finger domain of IKK gamma block the activation of NF-kappa B and the induction of IL-2 in stimulated T lymphocytes". Shifera, Amde Selassie; Horwitz Marshall S (March 2008). Mol. Immunol. (England) 45 (6): 1633–45. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2007.09.036. PMID 18207244.
(5) Expanding the substantial interactome of NEMO using protein microarrays. Fenner BJ, Scannell M, Prehn JH. PLoS One. 2010 Jan 20;5(1):e8799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008799. PMID: 20098747 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Free PMC Article
(6) A beginner's guide to NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Delhalle S, Blasius R, Dicato M, Diederich M. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1030:1-13. Review. PMID: 15659775 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
(7) "TNF-induced recruitment and activation of the IKK complex require Cdc37 and Hsp90". Chen G, Cao P, Goeddel DV (2002). Mol. Cell 9 (2): 401–10. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00450-1. PMID 11864612.
(8) "NEMO recognition of ubiquitinated Bcl10 is required for T cell receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation". Wu CJ, Ashwell JD (February 2008). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 (8): 3023–8. PMID 18287044.
(9) Inhibition of NF-kappa Bactivation by peptidestargetingNF-kappa Bessentialmodulator (nemo) oligomerization. Agou F, Courtois G, Chiaravalli J, Baleux F, Coïc YM, Traincard F, Israël A, Véron M. J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 24;279(52):54248-57. Epub 2004 Oct 5. PMID: 15466857 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Free Article